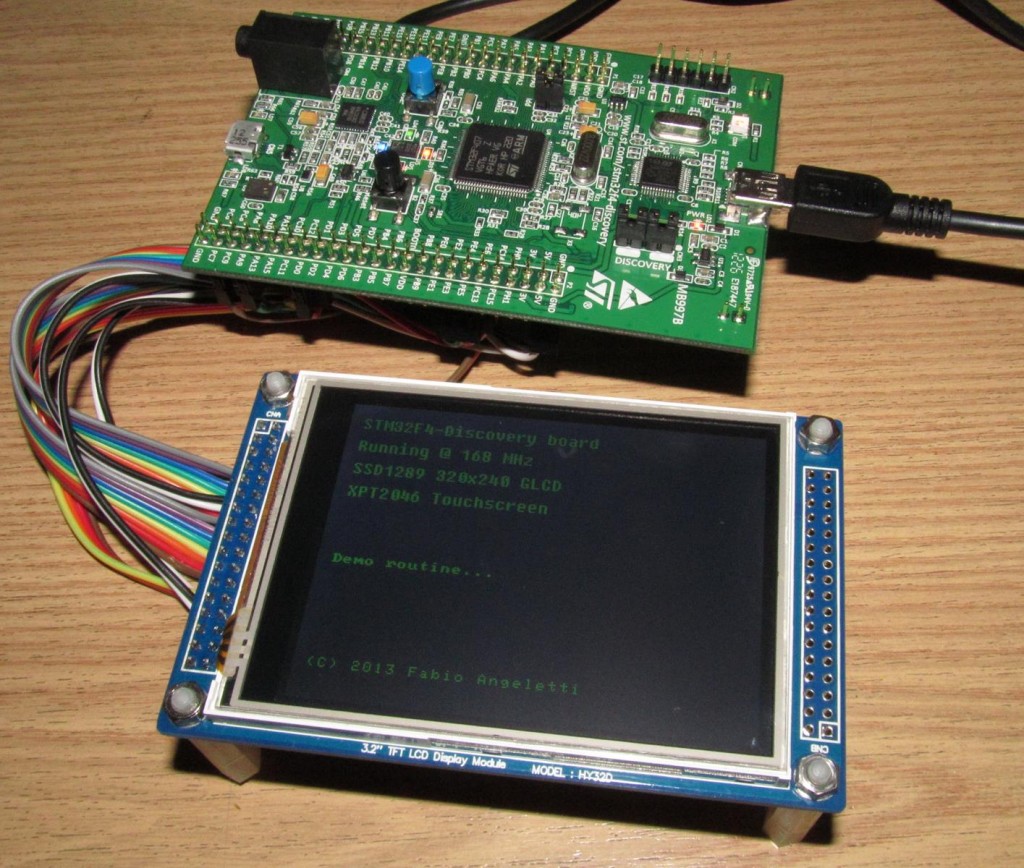
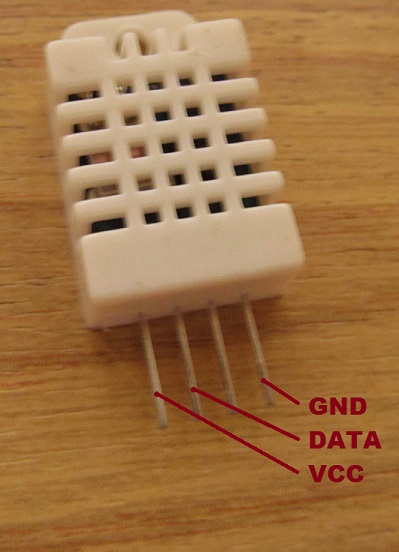
The DHT22 (also known as AM2302) is a cheap temperature and humidity sensor with an impressive performance! It uses a capacitive humidity sensor and a thermistor to measure the air, and send out a digital signal on the data pin (no analog input pins needed). Its fairly simple to use, but requires careful timing to grab data. The only real CON of this sensor is that you can only get new data from it once every 2 seconds. It is provided with a single wire digital interface. The sensor is calibrated and only requires a single pull-up resistor (any value between 3.6k and 10k should work fine) on the dataline to communicate correctly. Compared to the cheaper (and wider diffused) DHT11, this module is much more precise, more accurate and works in a bigger range of temperature/humidity.
Continue reading →